

- #Pdf cdf pdf
- #Pdf cdf iso
Another property is the PDF is defined across the entire sample space. The PDF also has the property that the area under the curve for is one. Like a histogram, the PDF when plotted reveals the shape of the distribution. 5-day Reliability Black Belt ® Live CourseĪs you may recall the probability density function describes the behavior of a random variable.5-day Reliability Green Belt ® Live Course.Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process course.An Introduction to Reliability Engineering.Reliability Analysis Methods online course.
#Pdf cdf iso
Risk Management Using ISO 31000 Course Landing Page.14 Ways to Acquire Reliability Engineering Knowledge.Reliability Engineering Management DRAFT.Innovative Thinking in Reliability and Durability.Equipment Risk and Reliability in Downhole Applications.Musings on Reliability and Maintenance Topics.
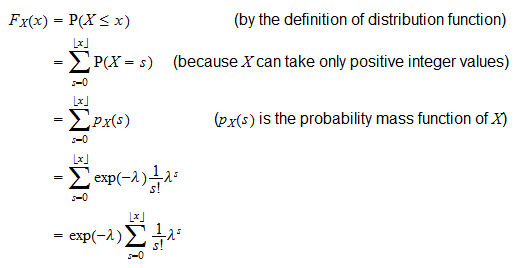 Metals Engineering and Product Reliability. Product Development and Process Improvement. Rooted in Reliability: The Plant Performance Podcast. We have also seen the python example to plot the PDF and CDF plot for the given data. In this post, we have understood different terms such as PMF, PDF, and CDF which are used very frequently when there is a talk about the probability distribution. NOTE: Now in seaborn, we have a function ecdfplot() to plot ecdf plot. Plt.plot(x_std3, y_std3, marker='.', linestyle='none') Plt.plot(x_std1, y_std1, marker='.', linestyle='none') Let's plot the CDF curve for the same data used above to plot the PDF curve. # Make a legend, set limits and show plot Plt.hist(samples_std10, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) Plt.hist(samples_std3, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) Plt.hist(samples_std1, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) # stds of interest: samples_std1, samples_std3, samples_std10 Plotting PDF Curve # Draw 100000 samples from Normal distribution with Now we know what PDF and CDF are let's see how we can plot PDF and CDF curves in Python. On the other hand, PDF is the probability density function for both discrete & continuous variables. PDF looks at probability at one point whereas, CDF is the total probability of anything below it.ĬDF is the cumulative density function that is used for continuous types of variables. Probability Distribution Function (PDF) vs Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) The primary difference between PMF and PDF is, The probability mass function (PMF) is usually the primary component of defining a discrete probability distribution, but it differs from the probability density function (PDF) where it produces distinct outcomes (or in other words continuous variables). Probability Mass Function (PMF) and Probability Density Function (PDF) Let's consider X as a discrete random variable for the function, then the general formula for probability mass function is as follows: –įor all x belonging to range of X. After the computation of all the probabilities, we can compute the probability distribution of the given random variable. Probability Mass Function, also called Discrete Density Function will allow us to find out the probability of getting a boost/interaction on a social media platform for each hour of the day i.e. Therefore, the random variable will take values ranging from 1 to 24. Now as there can be only 24 hours in the day. Let's understand this with the help of an example. Suppose we have to figure out at which hour of the day has more probability of getting a boost/interaction on social media platforms such as LinkedIn, provided we have some related data. We know that there are different types of distributions for discrete and continuous variables: A complete guide to the Probability Distribution and for every distribution, the formula of probability mass function varies. P(X) where X is a random variable is known as probability mass function, where a random variable can be: Probability mass function also called as probability function or frequency function is defined as a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. Next, let's move forward and understand how we can use PMF to calculate the probabilities of a random variable whether it is discrete or continuous. Now, to calculate the probability of a random variable with its value equal to some value within the range, Probability Mass Function (PMF) is used. In our earlier post A complete guide to the Probability Distribution, we have developed a deep understanding of the different types of discrete and continuous possible probability distributions.
Metals Engineering and Product Reliability. Product Development and Process Improvement. Rooted in Reliability: The Plant Performance Podcast. We have also seen the python example to plot the PDF and CDF plot for the given data. In this post, we have understood different terms such as PMF, PDF, and CDF which are used very frequently when there is a talk about the probability distribution. NOTE: Now in seaborn, we have a function ecdfplot() to plot ecdf plot. Plt.plot(x_std3, y_std3, marker='.', linestyle='none') Plt.plot(x_std1, y_std1, marker='.', linestyle='none') Let's plot the CDF curve for the same data used above to plot the PDF curve. # Make a legend, set limits and show plot Plt.hist(samples_std10, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) Plt.hist(samples_std3, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) Plt.hist(samples_std1, normed=True, histtype='step', bins=100) # stds of interest: samples_std1, samples_std3, samples_std10 Plotting PDF Curve # Draw 100000 samples from Normal distribution with Now we know what PDF and CDF are let's see how we can plot PDF and CDF curves in Python. On the other hand, PDF is the probability density function for both discrete & continuous variables. PDF looks at probability at one point whereas, CDF is the total probability of anything below it.ĬDF is the cumulative density function that is used for continuous types of variables. Probability Distribution Function (PDF) vs Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) The primary difference between PMF and PDF is, The probability mass function (PMF) is usually the primary component of defining a discrete probability distribution, but it differs from the probability density function (PDF) where it produces distinct outcomes (or in other words continuous variables). Probability Mass Function (PMF) and Probability Density Function (PDF) Let's consider X as a discrete random variable for the function, then the general formula for probability mass function is as follows: –įor all x belonging to range of X. After the computation of all the probabilities, we can compute the probability distribution of the given random variable. Probability Mass Function, also called Discrete Density Function will allow us to find out the probability of getting a boost/interaction on a social media platform for each hour of the day i.e. Therefore, the random variable will take values ranging from 1 to 24. Now as there can be only 24 hours in the day. Let's understand this with the help of an example. Suppose we have to figure out at which hour of the day has more probability of getting a boost/interaction on social media platforms such as LinkedIn, provided we have some related data. We know that there are different types of distributions for discrete and continuous variables: A complete guide to the Probability Distribution and for every distribution, the formula of probability mass function varies. P(X) where X is a random variable is known as probability mass function, where a random variable can be: Probability mass function also called as probability function or frequency function is defined as a function that gives the probability that a discrete random variable is exactly equal to some value. Next, let's move forward and understand how we can use PMF to calculate the probabilities of a random variable whether it is discrete or continuous. Now, to calculate the probability of a random variable with its value equal to some value within the range, Probability Mass Function (PMF) is used. In our earlier post A complete guide to the Probability Distribution, we have developed a deep understanding of the different types of discrete and continuous possible probability distributions.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
